Lean Six Sigma is a method that relies on a collaborative team effort to improve performance by systematically removing waste and reducing variation.
Lean is a systematic approach to reduce or eliminate activities that don’t add value to the process, i.e. waste. It emphasizes removing wasteful steps in a process by keeping only the value added steps. The Lean method ensures high quality and customer satisfaction.
Six Sigma is a data-driven problem-solving methodology. The focus is on process variations and emphasis is given to customer satisfaction. Continuous process improvement with low defects (ultimately 1 in a million) is the goal of this method.
Lean Six Sigma combines the strategies of Lean and Six Sigma. Lean principles help to reduce or eliminate process wastes. Six Sigma focuses on variation reduction in processes. Thereby, the principles of Lean Six Sigma help to improve the efficiency and quality of the process.
In today’s very dynamic environment a Lean or Six Sigma approach cannot bring full potential to improvements if applied in isolation. Integration of Lean & Six Sigma ensures exceptional improvements. In this management approach, traditionally the lean methodology is used first to remove the waste in a process. Later, the Six Sigma tools are used to improve process variations. However, these two methods go hand in hand in today’s time.
The ultimate objective is to improve processes by reducing variation and eliminating waste. It’s a continuous improvement process, where Lean methods and Six Sigma approaches, both take their turn during PDCA. The extent of approaches may differ depending upon process complexities or improvement sought. The combination of these two methods helps to develop streamlined processes with high quality & results. It improves bottom-line profits and helps meeting business goals.
The integrated Lean Six Sigma management approach is being used across sectors and industries. It promotes to exceptional changes in organization’s performance. Lean Six Sigma leads to enjoying competitive advantages in various companies in the world. They can be product or service-oriented companies. For both the LSS methodology improves their processes and makes them efficient. The key to success is management support, employee engagement and commitment to improving customer satisfaction.
As Deming liked to point out, a production line could be producing products with zero defects yet the business could still be failing. People don’t buy products because they’re zero defects per million. People buy products because of their wants and needs. As such, it’s important to recognize that the design for six sigma (DFSS) approach lays the necessary theoretical grounding for the DMAIC process to build upon. Six Sigma requires processes like DFSS to kick off the cycle.
When your company designs a new product or process from the ground up it requires a sizable amount of time and resources. Many products today are highly complex, providing multiple opportunities for things to go wrong. If your design does not meet the customer’s actual wants and expectations or your product does not provide the value the customer is willing to pay for, the product sales will suffer. Redesigning products and processes draws heavily on your resources and increases your time to market.
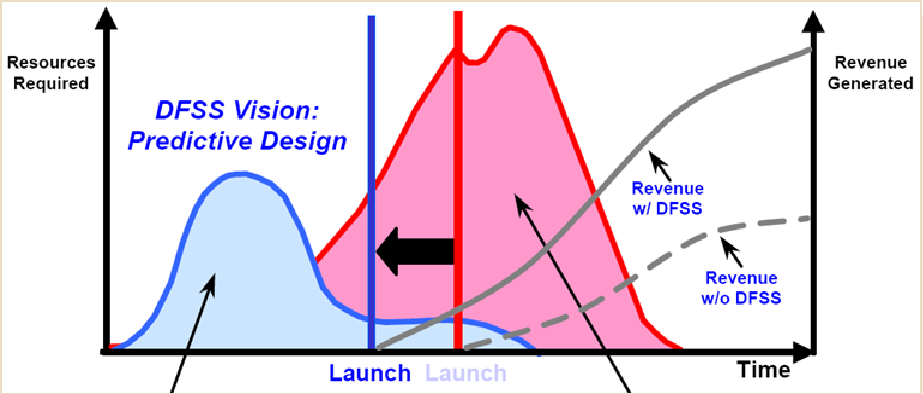
Multiple redesigns of a product are expensive and wasteful. It would be much more beneficial if the product met the actual needs and expectations of the customer, with a higher level of product quality the first time. Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) focuses on performing additional work up front to assure you fully understand the customer’s needs and expectations prior to design completion.
While Six Sigma is a rigorous methodology to improve existing products and/or processes, Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) is more an approach to new product or process development in that there are multiple methodologies that can be utilized. There are however, some fundamental characteristics that each of these methodologies share. The DFSS project should involve a cross functional team from the entire organization. It is a team effort that should be focused on the customer requirements and Critical to Quality parameters (CTQs). The DFSS team should invest time studying and understanding the issues with the existing systems prior to developing a new design.
As mentioned above, unlike the DMAIC methodology in Six Sigma, the phases or steps of DFSS are not universally recognized or defined — almost every company or training organization will define DFSS differently. One popular Design for Six Sigma methodology is called DMADV, (Define, Measure, Analyse, Design, Verify), another well-known design methodology, especially in the manufacturing world, is IDOV (Identify, Design, Optimize, Validate).
In all cases DFSS is used to design or re-design a product or service from the ground up. The expected process Sigma level for a DFSS product or service is at least 4.5 (no more than approximately 1 defect per thousand opportunities), but can be 6 Sigma or higher depending the product. Producing such a low defect level from product or service launch means that customer expectations and needs (CTQs) must be completely understood before a design can be completed and implemented.
So the DFSS approach can utilize any of the many possible methodologies. The fact is that all of these DFSS methodologies use the same advanced design tools (Quality Function Deployment, Failure Modes and Effects Analysis, benchmarking, Design of Experiments, simulation, statistical optimization, error proofing, Robust Design, etc.). Each methodology primarily differs in the name of each phase and the number of phases (and, of course, the acronym).
How do you decide which DFSS methodology to use? If you’re hiring a consulting company to help with your deployment, use their methodology as their training materials will be tailored around it. If you are implementing DFSS on your own, any of the DFSS books available should get you moving in the right direction. In any case, following a detailed DFSS methodology will help you achieve high quality levels for new products and services. If you are interested in improving your existing products or services, DMAIC is a more appropriate methodology to use.
By utilizing Design for Six Sigma methodologies, companies have reduced their time to market by 25 to 40 percent while providing a high quality product that does meet the customer’s requirements. DFSS is a proactive approach to design with quantifiable data and proven design tools that can improve your chances of success.